Machine Learning algorithm on Spark
page rank and decision tree on spark
PageRank
算法
The PageRank algorithm outputs a probability distribution used to represent the likelihood that a person randomly clicking on links will arrive at any particular page.
- Initialize each page’s rank to 1.0.
- On each iteration, have page p send a contribution of rank(p)/numNeighbors(p) to its neighbors (the pages it has links to).
- Set each page’s rank to 0.15 + 0.85 * contributionsReceived.
The last two steps repeat for several iterations, during which the algorithm will con‐ verge to the correct PageRank value for each page. In practice, it’s typical to run about 10 iterations.
实例
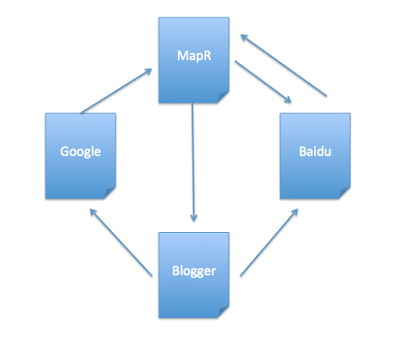
Above diagram shows there are 4 web pages with theirs outboundlinks.
("MapR",List("Baidu","Blogger")),
("Baidu", List("MapR")),
("Blogger",List("Google","Baidu")),
("Google", List("MapR"))
Solution:
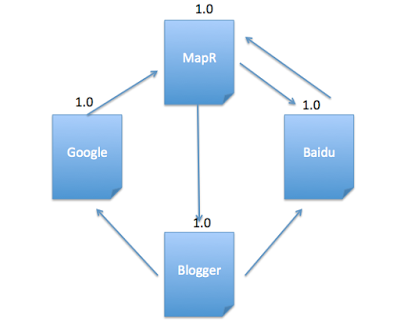
Initialize each page’s rank to 1.0.
val links = sc.parallelize(List(("MapR",List("Baidu","Blogger")),("Baidu", List("MapR")),("Blogger",List("Google","Baidu")),("Google", List("MapR")))).partitionBy(new HashPartitioner(4)).persist()
var ranks = links.mapValues(v => 1.0)
On each iteration, have page p send a contribution of rank(p)/numNeighbors(p) to its neighbors (the pages it has links to).
val contributions = links.join(ranks).flatMap { case (url, (links, rank)) => links.map(dest => (dest, rank / links.size)) }
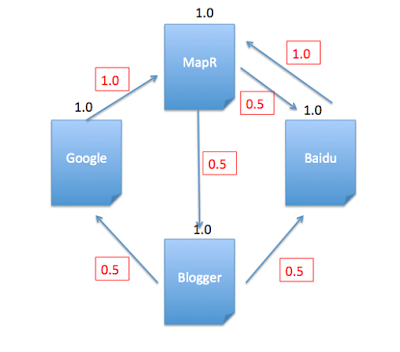
See above contributions in red, and it matches the calculations using scala:
scala> contributions.collect
res26: Array[(String, Double)] = Array((MapR,1.0), (Baidu,0.5), (Blogger,0.5), (Google,0.5), (Baidu,0.5), (MapR,1.0))
Set each page’s rank to 0.15 + 0.85 * contributionsReceived.
val ranks = contributions.reduceByKey((x, y) => x + y).mapValues(v => 0.15 + 0.85*v)
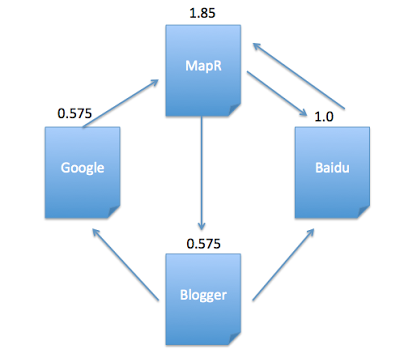
After 1st iteration, current pagerank value for each page is:
scala> ranks.collect
res27: Array[(String, Double)] = Array((Google,0.575), (MapR,1.8499999999999999), (Blogger,0.575), (Baidu,1.0))
Then the last two steps repeat for several iterations.
Decision Tree
概率统计理论
信息量的数学定义为: $$ I(u_i)=-log_2P(u_i) $$ 其中 $$P(u_i)$$ 为信息 $$ui$$ 发生的概率。信息熵是信息量的数学期望,是信源发出信息前的平均不确定性,也成为先验熵,信息熵的数学定义为:
$$Ent(U)=-\sum_iP(u_i)log_2P(u_i)$$
当已知信号U的概率分布P(U)且收到信号$$V=v_i$$后,发出信号的概率分布变为\(P(U|v_j)\),于是信源的平均不确定性变为(也称为条件熵):
$$Ent(U|v_i)=-\sum_iP(u_i|v_i)log_2P(u_i|v_i)$$
信息增益为:
$$Gains(U,V)=Ent(U)-Ent(U|V)$$
ID3
ID3算法的主要思想就是每次计算出各个属性的信息增益,选择最大者为分裂属性。下面举例说明,为简单起见,随机杜撰了10条数据,分为2个维度:
性别(T1) |1 |0 |1 |0 |1 |0 |1 |0 |1 |1 套餐类别(T2) |A |B |A |A |C |C |B |A |A |C 是否购买 |true |false |true |false |true |true |false |true |true |true
信息熵: $$ Ent(U)=-\sum_iP(u_i)log_2P(u_i)=-{7\over 10}log_2({7\over 10})-{3\over 10}log_2({3\over 10})=0.881 $$
条件熵 $$ Ent(U|T_1)={6\over 10}(-{5\over 6}log_2({5\over 6})-{1\over 6}log_2({1\over 6}))+{4\over 10}(-{2\over 4}log_2({2\over 4})-{2\over 4}log_2({2\over 4}))=0.790 $$
$$ Ent(U|T_2)={5\over 10}(-{4\over 5}log_2({4\over 5})-{1\over 5}log_2({1\over 5}))+{2\over 10}(-{2\over 2}log_2({2\over 2})-{0\over 2}log_2({0\over 2}))+{3\over 10}(-{3\over 3}log_2({3\over 3})-{0\over 3}log_2({0\over 3}))=0.361 $$
信息增益 $$ Gains(U,T_1)=Ent(U)-Ent(U|T_1)=0.091 $$
$$ Gains(U,T_2)=Ent(U)-Ent(U|T_2)=0.520 $$
根据ID3的算法,目前来说这种情况下将会选择T2作为最佳分组变量,因为它消除信宿对信源的平均不确定性的能力最强,由此得到T2->T1的树结构
Spark实例 ###
categoricalFeaturesInfospecifies which features are categorical and how many categorical values each of those features can take. This is given as a map from feature index to the number of categories for that feature. Any features not in this map are treated as continuous.- e.g:For the test data,the first categorical feature, categoricalFeaturesInfo = (0 -> 31) specifies that feature index 0 (which represents the day of the month) has 31 categories (values {0, …, 31}). The second , categoricalFeaturesInfo = (1 -> 7), represents days of the week, and specifies that feature index 1 has 7 categories. The carrier categorial feature is index 4 and the value can go from 0 to the number of distinct carriers , and so on.
maxDepthMaximum depth of a tree.maxBinsNumber of bins used when discretizing continuous features.- Note that the maxBins parameter must be at least the maximum number of categories MM for any categorical feature
numClassesNumber of classes (for Classification only).impurityImpurity measure of the homogeneity of the labels at the node
import org.apache.spark._
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
import org.apache.spark.util.IntParam
// Import classes for MLLib regression labeledpoint, vectors, decisiontree, decisiontree model, MLUtils
import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LabeledPoint
import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors
import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.DecisionTree
import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.model.DecisionTreeModel
import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils
case class Flight(dofM: String, dofW: String, carrier: String, tailnum: String, flnum: Int, org_id: String, origin: String, dest_id: String, dest: String, crsdeptime: Double, deptime: Double, depdelaymins: Double, crsarrtime: Double, arrtime: Double, arrdelay: Double, crselapsedtime: Double, dist: Int)
// function to parse input into Movie class
def parseFlight(str: String): Flight = {
val line = str.split(",")
Flight(line(0), line(1), line(2), line(3), line(4).toInt, line(5), line(6), line(7), line(8), line(9).toDouble, line(10).toDouble, line(11).toDouble, line(12).toDouble, line(13).toDouble, line(14).toDouble, line(15).toDouble, line(16).toInt)
}
//Creating and RDD with the January 2014 data to be used for training the model
val textRDD = sc.textFile("/user/user01/data/rita2014jan.csv")
val flightsRDD = textRDD.map(parseFlight).cache()
flightsRDD.take(2)
//Array(Flight(1,3,AA,N338AA,1,12478,JFK,12892,LAX,900.0,914.0,14.0,1225.0,1238.0,13.0,385.0,2475),
// Flight(2,4,AA,N338AA,1,12478,JFK,12892,LAX,900.0,857.0,0.0,1225.0,1226.0,1.0,385.0,2475))
var carrierMap: Map[String, Int] = Map()
var index: Int = 0
flightsRDD.map(flight => flight.carrier).distinct.collect.foreach(x => { carrierMap += (x -> index); index += 1 })
carrierMap.toString
//res2: String = Map(DL -> 5, F9 -> 10, US -> 9, OO -> 2, B6 -> 0, AA -> 6, EV -> 12, FL -> 1, UA -> 4, MQ -> 8, WN -> 13, AS -> 3, VX -> 7, HA -> 11)
var originMap: Map[String, Int] = Map()
var index1: Int = 0
flightsRDD.map(flight => flight.origin).distinct.collect.foreach(x => { originMap += (x -> index1); index1 += 1 })
originMap.toString
//res4: String = Map(JFK -> 214, LAX -> 294, ATL -> 273,MIA -> 175 ...
var destMap: Map[String, Int] = Map()
var index2: Int = 0
flightsRDD.map(flight => flight.dest).distinct.collect.foreach(x => { destMap += (x -> index2); index2 += 1 })
//- Defining the features array
val mlprep = flightsRDD.map(flight => {
val monthday = flight.dofM.toInt - 1 // category
val weekday = flight.dofW.toInt - 1 // category
val crsdeptime1 = flight.crsdeptime.toInt
val crsarrtime1 = flight.crsarrtime.toInt
val carrier1 = carrierMap(flight.carrier) // category
val crselapsedtime1 = flight.crselapsedtime.toDouble
val origin1 = originMap(flight.origin) // category
val dest1 = destMap(flight.dest) // category
val delayed = if (flight.depdelaymins.toDouble > 40) 1.0 else 0.0
Array(delayed.toDouble, monthday.toDouble, weekday.toDouble, crsdeptime1.toDouble, crsarrtime1.toDouble, carrier1.toDouble, crselapsedtime1.toDouble, origin1.toDouble, dest1.toDouble)
})
mlprep.take(1)
//res6: Array[Array[Double]] = Array(Array(0.0, 0.0, 2.0, 900.0, 1225.0, 6.0, 385.0, 214.0, 294.0))
//Making LabeledPoint of features - this is the training data for the model
val mldata = mlprep.map(x => LabeledPoint(x(0), Vectors.dense(x(1), x(2), x(3), x(4), x(5), x(6), x(7), x(8))))
mldata.take(1)
//res7: Array[org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LabeledPoint] = Array((0.0,[0.0,2.0,900.0,1225.0,6.0,385.0,214.0,294.0]))
// mldata0 is %85 not delayed flights
val mldata0 = mldata.filter(x => x.label == 0).randomSplit(Array(0.85, 0.15))(1)
// mldata1 is %100 delayed flights
val mldata1 = mldata.filter(x => x.label != 0)
// mldata2 is delayed and not delayed
val mldata2 = mldata0 ++ mldata1
mldata2.count
res27: Long = 116692
// split mldata2 into training and test data
val splits = mldata2.randomSplit(Array(0.7, 0.3))
val (trainingData, testData) = (splits(0), splits(1))
trainingData.count
res26: Long = 81727
// set ranges for 0=dofM 1=dofW 4=carrier 6=origin 7=dest
var categoricalFeaturesInfo = Map[Int, Int]()
categoricalFeaturesInfo += (0 -> 31)
categoricalFeaturesInfo += (1 -> 7)
categoricalFeaturesInfo += (4 -> carrierMap.size)
categoricalFeaturesInfo += (6 -> originMap.size)
categoricalFeaturesInfo += (7 -> destMap.size)
val numClasses = 2
// Defning values for the other parameters
val impurity = "gini"
val maxDepth = 9
val maxBins = 7000
val model = DecisionTree.trainClassifier(trainingData, numClasses, categoricalFeaturesInfo,
impurity, maxDepth, maxBins)
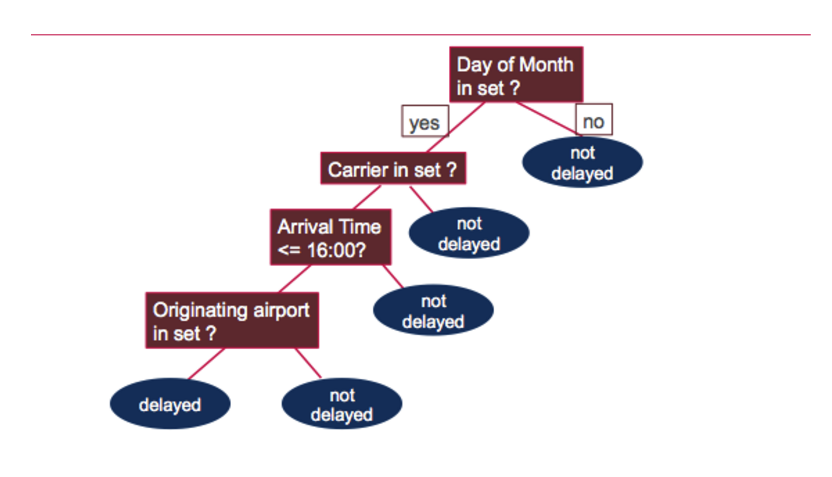
model.toDebugString
// 0=dofM 4=carrier 3=crsarrtime1 6=origin
res20: String =
DecisionTreeModel classifier of depth 9 with 919 nodes
If (feature 0 in {11.0,12.0,13.0,14.0,15.0,16.0,17.0,18.0,19.0,20.0,21.0,22.0,23.0,24.0,25.0,26.0,27.0,30.0})
If (feature 4 in {0.0,1.0,2.0,3.0,4.0,5.0,6.0,7.0,8.0,9.0,10.0,11.0,13.0})
If (feature 3 <= 1603.0)
If (feature 0 in {11.0,12.0,13.0,14.0,15.0,16.0,17.0,18.0,19.0})
If (feature 6 in {0.0,1.0,2.0,3.0,4.0,5.0,6.0,7.0,8.0,10.0,11.0,12.0,13.0...
testData.take(1)
//res21: Array[org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LabeledPoint] = Array((0.0,[18.0,6.0,900.0,1225.0,6.0,385.0,214.0,294.0]))
val labelAndPreds = testData.map { point =>
val prediction = model.predict(point.features)
(point.label, prediction)
}
labelAndPreds.take(3)
res33: Array[(Double, Double)] = Array((0.0,0.0), (0.0,0.0), (0.0,0.0))
val wrongPrediction =(labelAndPreds.filter{
case (label, prediction) => ( label !=prediction)
})
wrongPrediction.count()
res35: Long = 11040
val ratioWrong=wrongPrediction.count().toDouble/testData.count()
ratioWrong: Double = 0.3157443157443157
testData.count
//res28: Long = 34965
// find delay predicted when there was no delay
val falsePositives =(labelAndPreds.filter{
case (label, prediction) => ( label==0 && prediction == 1)
})
falsePositives.count
//res24: Long = 5489
val falseNegatives =(labelAndPreds.filter(r => ( r._2==0 && r._1== 1) ))
falseNegatives.count
//res34: Long = 5551
val fpRatio=falsePositives.count.toDouble/ testData.count()
fpRatio: Double = 0.156985556985557
val fnRatio=falseNegatives.count.toDouble/ testData.count()
fnRatio: Double = 0.15875875875875875
Model.toDebugString prints out the decision tree, which asks the following questions to determine if the flight was delayed or not: