leetcode
leetcode部分题解
subarray-sum-equals-k
https://leetcode.com/problems/subarray-sum-equals-k/description/
题目描述
Given an array of integers and an integer k, you need to find the total number of continuous subarrays whose sum equals to k.
Example 1:
Input:nums = [1,1,1], k = 2
Output: 2
Note:
The length of the array is in range [1, 20,000].
The range of numbers in the array is [-1000, 1000] and the range of the integer k is [-1e7, 1e7].
思路
符合直觉的做法是暴力求解所有的子数组,然后分别计算和,如果等于k,count就+1.这种做法的时间复杂度为O(n^2).
这里有一种更加巧妙的方法,我们可以借助额外的空间,使用hashmap来简化时间复杂度,这种算法的时间复杂度可以达到O(n).
我们维护一个hashmap,hashmap的key为累加值acc,value为累加值acc出现的次数。 我们迭代数组,然后不断更新acc和hashmap,如果acc 等于k,那么很明显应该+1. 如果hashmap[acc - k] 存在, 我们就把它加到结果中去即可。
语言比较难以解释,我画了一个图来演示nums = [1,2,3,3,0,3,4,2], k = 6的情况。
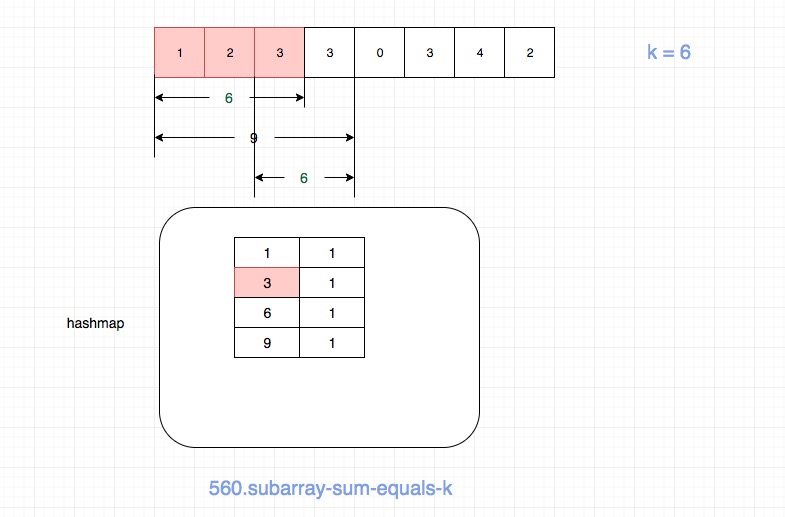
如图,当访问到nums[3]的时候,hashmap如图所示,这个时候count为2. 其中之一是[1,2,3],这个好理解。还有一个是[3,3].
这个[3,3]正是我们通过hashmap[acc - k]即hashmap[9 - 6]得到的。
关键点解析
- 可以利用hashmap记录和的累加值来避免重复计算
代码
- 语言支持:JS, Python
Javascript Code:
/*
* @lc app=leetcode id=560 lang=javascript
*
* [560] Subarray Sum Equals K
*/
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @param {number} k
* @return {number}
*/
var subarraySum = function(nums, k) {
const hashmap = {};
let acc = 0;
let count = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
acc += nums[i];
if (acc === k) count++;
if (hashmap[acc - k] !== void 0) {
count += hashmap[acc - k];
}
if (hashmap[acc] === void 0) {
hashmap[acc] = 1;
} else {
hashmap[acc] += 1;
}
}
return count;
};
Python Code:
class Solution:
def subarraySum(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> int:
d = {}
acc = count = 0
for num in nums:
acc += num
if acc == k:
count += 1
if acc - k in d:
count += d[acc-k]
if acc in d:
d[acc] += 1
else:
d[acc] = 1
return count
jump-game
https://leetcode.com/problems/jump-game/description/
题目描述
Given an array of non-negative integers, you are initially positioned at the first index of the array.
Each element in the array represents your maximum jump length at that position.
Determine if you are able to reach the last index.
Example 1:
Input: [2,3,1,1,4]
Output: true
Explanation: Jump 1 step from index 0 to 1, then 3 steps to the last index.
Example 2:
Input: [3,2,1,0,4]
Output: false
Explanation: You will always arrive at index 3 no matter what. Its maximum
jump length is 0, which makes it impossible to reach the last index.
思路
这道题目是一道典型的回溯类型题目。
思路就是用一个变量记录当前能够到达的最大的索引,我们逐个遍历数组中的元素去更新这个索引。
变量完成判断这个索引是否大于数组下表即可。
关键点解析
- 建模 (记录和更新当前位置能够到达的最大的索引即可)
代码
- 语言支持: Javascript,Python3
/*
* @lc app=leetcode id=55 lang=javascript
*
* [55] Jump Game
*
* https://leetcode.com/problems/jump-game/description/
*
* algorithms
* Medium (31.38%)
* Total Accepted: 252.4K
* Total Submissions: 797.2K
* Testcase Example: '[2,3,1,1,4]'
*
* Given an array of non-negative integers, you are initially positioned at the
* first index of the array.
*
* Each element in the array represents your maximum jump length at that
* position.
*
* Determine if you are able to reach the last index.
*
* Example 1:
*
*
* Input: [2,3,1,1,4]
* Output: true
* Explanation: Jump 1 step from index 0 to 1, then 3 steps to the last
* index.
*
*
* Example 2:
*
*
* Input: [3,2,1,0,4]
* Output: false
* Explanation: You will always arrive at index 3 no matter what. Its
* maximum
* jump length is 0, which makes it impossible to reach the last index.
*
*
*/
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {boolean}
*/
var canJump = function(nums) {
let max = 0; // 能够走到的数组下标
for(let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (max < i) return false; // 当前这一步都走不到,后面更走不到了
max = Math.max(nums[i] + i, max);
}
return max >= nums.length - 1
};
Python3 Code:
class Solution:
def canJump(self, nums: List[int]) -> bool:
"""思路同上"""
_max = 0
_len = len(nums)
for i in range(_len-1):
if _max < i:
return False
_max = max(_max, nums[i] + i)
# 下面这个判断可有可无,但提交的时候数据会好看点
if _max >= _len - 1:
return True
return _max >= _len - 1
1014. 最佳观光组合
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-sightseeing-pair/description/
题目描述
给定正整数数组 A,A[i] 表示第 i 个观光景点的评分,并且两个景点 i 和 j 之间的距离为 j - i。
一对景点(i < j)组成的观光组合的得分为(A[i] + A[j] + i - j):景点的评分之和减去它们两者之间的距离。
返回一对观光景点能取得的最高分。
示例:
输入:[8,1,5,2,6] 输出:11 解释:i = 0, j = 2, A[i] + A[j] + i - j = 8 + 5 + 0 - 2 = 11
提示:
2 <= A.length <= 50000 1 <= A[i] <= 1000
思路
最简单的思路就是两两组合,找出最大的,妥妥超时,我们来看下代码:
class Solution:
def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, A: List[int]) -> int:
n = len(A)
res = 0
for i in range(n - 1):
for j in range(i + 1, n):
res = max(res, A[i] + A[j] + i - j)
return res
我们思考如何优化。 其实我们可以遍历一遍数组,对于数组的每一项A[j] - j 我们都去前面找最大的 A[i] + i (这样才能保证结果最大)。
我们考虑使用动态规划来解决, 我们使用 dp[i] 来表示 数组 A 前 i 项的A[i] + i的最大值。
class Solution:
def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, A: List[int]) -> int:
n = len(A)
dp = [float('-inf')] * (n + 1)
res = 0
for i in range(n):
dp[i + 1] = max(dp[i], A[i] + i)
res = max(res, dp[i] + A[i] - i)
return res
如上其实我们发现,dp[i + 1] 只和 dp[i] 有关,这是一个空间优化的信号。我们其实可以使用一个变量来记录,而不必要使用一个数组,代码见下方。
关键点解析
- 空间换时间
- dp 空间优化
代码
class Solution:
def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, A: List[int]) -> int:
n = len(A)
pre = A[0] + 0
res = 0
for i in range(1, n):
res = max(res, pre + A[i] - i)
pre = max(pre, A[i] + i)
return res
小技巧
Python 的代码如果不使用 max,而是使用 if else 效率目测会更高,大家可以试一下。
class Solution:
def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, A: List[int]) -> int:
n = len(A)
pre = A[0] + 0
res = 0
for i in range(1, n):
# res = max(res, pre + A[i] - i)
# pre = max(pre, A[i] + i)
res = res if res > pre + A[i] - i else pre + A[i] - i
pre = pre if pre > A[i] + i else A[i] + i
return res
merge-intervals
https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-intervals/description/
题目描述
Given a collection of intervals, merge all overlapping intervals.
Example 1:
Input: [[1,3],[2,6],[8,10],[15,18]]
Output: [[1,6],[8,10],[15,18]]
Explanation: Since intervals [1,3] and [2,6] overlaps, merge them into [1,6].
Example 2:
Input: [[1,4],[4,5]]
Output: [[1,5]]
Explanation: Intervals [1,4] and [4,5] are considered overlapping.
NOTE: input types have been changed on April 15, 2019. Please reset to default code definition to get new method signature.
思路
- 先对数组进行排序,排序的依据就是每一项的第一个元素的大小。
- 然后我们对数组进行遍历,遍历的时候两两运算(具体运算逻辑见下)
- 判断是否相交,如果不相交,则跳过
如果相交,则合并两项
关键点解析
对数组进行排序简化操作
如果不排序,需要借助一些hack,这里不介绍了
代码
- 语言支持: Javascript,Python3
/*
* @lc app=leetcode id=56 lang=javascript
*
* [56] Merge Intervals
*/
/**
* @param {number[][]} intervals
* @return {number[][]}
*/
function intersected(a, b) {
if (a[0] > b[1] || a[1] < b[0]) return false;
return true;
}
function mergeTwo(a, b) {
return [Math.min(a[0], b[0]), Math.max(a[1], b[1])];
}
var merge = function(intervals) {
// 这种算法需要先排序
intervals.sort((a, b) => a[0] - b[0]);
for (let i = 0; i < intervals.length - 1; i++) {
const cur = intervals[i];
const next = intervals[i + 1];
if (intersected(cur, next)) {
intervals[i] = undefined;
intervals[i + 1] = mergeTwo(cur, next);
}
}
return intervals.filter(q => q);
};
Python3 Code:
class Solution:
def merge(self, intervals: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
"""先排序,后合并"""
if len(intervals) <= 1:
return intervals
# 排序
def get_first(a_list):
return a_list[0]
intervals.sort(key=get_first)
# 合并
res = [intervals[0]]
for i in range(1, len(intervals)):
if intervals[i][0] <= res[-1][1]:
res[-1] = [res[-1][0], max(res[-1][1], intervals[i][1])]
else:
res.append(intervals[i])
return res
Others
reverse a linked list
# Python program to reverse a linked list
# Time Complexity : O(n)
# Space Complexity : O(1)
# Node class
class Node:
# Constructor to initialize the node object
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Function to reverse the linked list
def reverse(self):
prev = None
current = self.head
while(current is not None):
next = current.next
current.next = prev
prev = current
current = next
self.head = prev
# Function to insert a new node at the beginning
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
# Utility function to print the linked LinkedList
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
while(temp):
print temp.data,
temp = temp.next
# Driver program to test above functions
llist = LinkedList()
llist.push(20)
llist.push(4)
llist.push(15)
llist.push(85)
print "Given Linked List"
llist.printList()
llist.reverse()
print "\nReversed Linked List"
llist.printList()
Given linked list
85 15 4 20
Reversed Linked list
20 4 15 85
Find the middle point
public ListNode findMiddle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
Top K Frequent Elements
给定一个数组,求数组里出现频率最高的 K 个数字,比如对于数组 [1,1,1,2,2,3],K=2 时,返回 [1,2]。解决该问题的思路比较常规,首先用 hashmap 记录每个数字的出现频率,然后可以用 heap 来求出现频率最高的 k 个数字。
class Pair{
int num;
int count;
public Pair(int num, int count){
this.num=num;
this.count=count;
}
}
public class Solution {//基于map和SortedQ
public List<Integer> topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {
//count the frequency for each element
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for(int num: nums){
if(map.containsKey(num)){
map.put(num, map.get(num)+1);
}else{
map.put(num, 1);
}
}
// create a min heap
PriorityQueue<Pair> queue = new PriorityQueue<Pair>(new Comparator<Pair>(){
public int compare(Pair a, Pair b){
return a.count-b.count;
}
});
//maintain a heap of size k.
for(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry: map.entrySet()){
Pair p = new Pair(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
queue.offer(p);
if(queue.size()>k){
queue.poll();
}
}
//get all elements from the heap
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>();
while(queue.size()>0){
result.add(queue.poll().num);
}
//reverse the order
Collections.reverse(result);
return result;
}
}
class Solution(object):
def topKFrequent(self, nums, k):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type k: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
counts = collections.Counter(nums)
heap = []
for key, cnt in counts.items():
if len(heap) < k:
heapq.heappush(heap, (cnt, key))
else:
if heap[0][0] < cnt:
heapq.heappop(heap)
heapq.heappush(heap, (cnt, key))
return [x[1] for x in heap]
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II
假设有一个数组,它的第i个元素是一个给定的股票在第i天的价格。设计一个算法来找到最大的利润。你可以完成尽可能多的交易(多次买卖股票)。然而,你不能同时参与多个交易(你必须在再次购买前出售股票)。给出一个数组样例[2,1,2,0,1], 1买入,2卖出.0买入,1卖出.返回 2
class Solution:
"""
@param prices: Given an integer array
@return: Maximum profit
"""
def maxProfit(self, prices):
# write your code here
total = 0
low, high = sys.maxint, sys.maxint
for x in prices:
if x > high:
high = x
else:
total += high - low
high, low = x, x
return total + high - low
public class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int profit = 0;
//从头到尾扫描prices,如果price[i] – price[i-1]大于零则计入最后的收益中。即贪心法
for (int i = 0; i < prices.length - 1; i++) {
int diff = prices[i+1] - prices[i];
if (diff > 0) {
profit += diff;
}
}
return profit;
}
}
Implement atoi to convert a string to an integer
following cases should be considered
- null or empty string
- white spaces
- +/- sign
- calculate real value
- handle min & max
public int atoi(String str) {
if (str == null || str.length() < 1)
return 0;
// trim white spaces
str = str.trim();
char flag = '+';
// check negative or positive
int i = 0;
if (str.charAt(0) == '-') {
flag = '-';
i++;
} else if (str.charAt(0) == '+') {
i++;
}
// use double to store result
double result = 0;
// calculate value
while (str.length() > i && str.charAt(i) >= '0' && str.charAt(i) <= '9') {
result = result * 10 + (str.charAt(i) - '0');
i++;
}
if (flag == '-')
result = -result;
// handle max and min
if (result > Integer.MAX_VALUE)
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if (result < Integer.MIN_VALUE)
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
return (int) result;
}
import re
class Solution(object):
def myAtoi(self, str):
"""
:type str: str
:rtype: int
"""
m = re.match(r'(\s)*(\+|\-|)(\d)*', str)
try:
s = int(m.group(0))
return min(max(s, -2147483648), 2147483647)
except:
return 0
Increasing Triplet Subsequence
Given an unsorted array return whether an increasing subsequence of length 3 exists or not in the array.Return true if there exists i, j, k such that arr[i] < arr[j] < arr[k] given 0 ≤ i < j < k ≤ n-1 else return false.
class Solution(object):
def increasingTriplet(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: bool
"""
x1 = x2 = 0x7fffffff
for num in nums:
if num <= x1:
x1 = num
elif num <= x2: # x1 < num <= x2
x2 = num
else: # x < x2 < num , so it return true
return True
return False
Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array
Given a sorted array, remove the duplicates in place such that each element appear only once and return the new length. Do not allocate extra space for another array, you must do this in place with constant memory. For example, Given input array A = [1,1,2], Your function should return length = 2, and A is now [1,2].
class Solution:
"""
@param A: a list of integers
@return an integer
"""
def removeDuplicates(self, A):
# write your code here
if A == []:
return 0
count = 0
for i in range(0, len(A)):
if A[i] == A[i-1]:
continue
else:
A[count] = A[i]
count += 1
return count
whether an integer is a palindrome
Determine whether an integer is a palindrome. Do this without extra space.
class Solution:
# @return a boolean
def isPalindrome(self, x):
if x < 0:
return False
div = 1
while x/div >= 10:
div = div * 10
while x:
left = x / div
right = x % 10
if left != right:
return False
x = ( x % div ) / 10
div = div / 100
return True
Search a 2D Matrix II
Write an efficient algorithm that searches for a value in an m x n matrix. This matrix has the following properties:
- Integers in each row are sorted in ascending from left to right.
- Integers in each column are sorted in ascending from top to bottom.
Consider the following matrix:
[
[1, 4, 7, 11, 15],
[2, 5, 8, 12, 19],
[3, 6, 9, 16, 22],
[10, 13, 14, 17, 24],
[18, 21, 23, 26, 30]
]
Given target = 5, return true. Given target = 20, return false.
# O(m+n)
class Solution:
# @param {integer[][]} matrix
# @param {integer} target
# @return {boolean}
def searchMatrix(self, matrix, target):
y = len(matrix[0]) - 1
for x in range(len(matrix)):
while y and matrix[x][y] > target:
y -= 1
if matrix[x][y] == target:
return True
return False
# O(m*logn)
class Solution:
# @param {integer[][]} matrix
# @param {integer} target
# @return {boolean}
def searchMatrix(self, matrix, target):
y = len(matrix[0]) - 1
def binSearch(nums, low, high):
while low <= high:
mid = (low + high) / 2
if nums[mid] > target:
high = mid - 1
else:
low = mid + 1
return high
for x in range(len(matrix)):
y = binSearch(matrix[x], 0, y)
if matrix[x][y] == target:
return True
return False
Swap Nodes in Pairs
Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head. For example, Given 1->2->3->4, you should return the list as 2->1->4->3. Your algorithm should use only constant space. You may not modify the values in the list, only nodes itself can be changed.
class Solution:
# @param head, a ListNode
# @return a ListNode
def swapPairs(self, head):
# Write your code here
if head == None or head.next == None:
return head
dummy = ListNode(0); dummy.next = head
p = dummy
while p.next and p.next.next:
tmp = p.next.next //store the second node as tmp
p.next.next = tmp.next //link first node to third node
tmp.next = p.next //link second node to first node
p.next = tmp //link p to the second
p = p.next.next // move p to the third
return dummy.next
public class Solution {
/**
* @param head a ListNode
* @return a ListNode
*/
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
head = dummy;
while (head.next != null && head.next.next != null) {
ListNode n1 = head.next, n2 = head.next.next;
// head->n1->n2->...
// => head->n2->n1->...
head.next = n2;
n1.next = n2.next;
n2.next = n1;
// move to next pair
head = n1;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
Count set bits in an integer
Input : n = 6
Output : 2
Binary representation of 6 is 110 and has 2 set bits
Input : n = 13
Output : 3
Binary representation of 13 is 1101 and has 3 set bits
Iterative Method to Count Set Bits
The iterative approach requires one iteration per bit. It runs utmost sizeof(int) number of times. Iteration terminates when no more bits are set. In worst case, on a 32-bit word with only the most significant bit set, it will loop through 32 iterations. This solution is the simplest one and useful if 1’s are sparse and among the least significant bits.
/* Iterative approach of counting set bits*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int countSetBits(unsigned int n)
{
unsigned int c; // the total bits set in n
for (c = 0; n; n >>= 1)
{
c += n & 1;
}
return c;
}
int main(void)
{
unsigned int n;
printf("Enter a positive integer: ");
scanf("%u", &n);
printf("%d\n", countSetBits(n));
}
Count Set Bits by Brian Kernighan’s Algorithm
Brian Kernighan’s algorithm every time performs a bitwise AND operation between inputted integer n and n-1 and keep c incrementing by 1 until n becomes zero. This solution iterates the number of set bits times through the loop. For example, if we input 17 then loop will iterate only two times, whereas in former solution (iterative method to count set bits) it would iterate 5 times.
Subtraction of 1 from a number toggles all the bits (from right to left) till the rightmost set bit(including the righmost set bit). So if we subtract a number by 1 and do bitwise & with itself (n & (n-1)), we unset the righmost set bit. If we do n & (n-1) in a loop and count the no of times loop executes we get the set bit count. Beauty of the this solution is number of times it loops is equal to the number of set bits in a given integer.
- Initialize count: = 0
- If integer n is not zero (a) Do bitwise & with (n-1) and assign the value back to n n: = n&(n-1) (b) Increment count by 1 © go to step 2
- Else return count
e.g countSetBits(9:1001) = 2
n = 9 (1001)
count = 0
Since 9 > 0, subtract by 1 and do bitwise & with (9-1)
n = 9&8 (1001 & 1000)
n = 8
count = 1
Since 8 > 0, subtract by 1 and do bitwise & with (8-1)
n = 8&7 (1000 & 0111)
n = 0
count = 2
Since n = 0, return count which is 2 now.
/* Brian Kernighan's algorithm of counting set bits*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int countSetBits(unsigned int n)
{
unsigned int c; // the total bits set in n
for (c = 0; n; n = n & (n-1))
{
c++;
}
return c;
}
int main(void)
{
unsigned int n;
printf("Enter a positive integer: ");
scanf("%u", &n);
printf("%d\n", countSetBits(n));
}
Coin Change
You are given coins of different denominations and a total amount of money amount. Write a function to compute the fewest number of coins that you need to make up that amount. If that amount of money cannot be made up by any combination of the coins, return -1.
Example 1:
coins = [1, 2, 5], amount = 11
return 3 (11 = 5 + 5 + 1)
Example 2:
coins = [2], amount = 3
return -1.
动态规划(Dynamic Programming)
状态转移方程:
Let dp[v] to be the minimum number of coins required to get the amount v.
dp[i+a_coin] = min(dp[i+a_coin], dp[i]+1) if dp[i] is reachable.
dp[i+a_coin] = dp[i+a_coin] is dp[i] is not reachable.
We initially set dp[i] to be -1.
//This solution takes time O(n^2).
class Solution(object):
def coinChange(self, coins, amount):
"""
:type coins: List[int]
:type amount: int
:rtype: int
"""
dp = [0] + [-1] * amount
for x in range(amount):
if dp[x] < 0:
continue
for c in coins:
if x + c > amount:
continue
if dp[x + c] < 0 or dp[x + c] > dp[x] + 1:
dp[x + c] = dp[x] + 1
return dp[amount]
广度优先搜索(BFS)
We maintain two queues: one of the amount so far(queue) and the other for the minimal steps for each amount(steps). The time is too much because of the contains method take n and total time is O(n^3).
class Solution(object):
def coinChange(self, coins, amount):
"""
:type coins: List[int]
:type amount: int
:rtype: int
"""
steps = collections.defaultdict(int)
queue = collections.deque([0])
steps[0] = 0
while queue:
front = queue.popleft()
level = steps[front]
if front == amount:
return level
for c in coins:
if front + c > amount:
continue
if front + c not in steps:
queue += front + c,
steps[front + c] = level + 1
return -1